Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
Volume 8 (4); 25 December, 2018In Vitro Antimicrobial Evaluation of Aqueus Methanol Extract from Calpurina Aurea (Fabaceae) Leaves.
Birhan M, Tessema T, Kenubih A and Yayeh M.
Asian J. Med. Pharm. Res., 8(4): 33-43, 2018; pii:S2252043018000005-8
Abstract
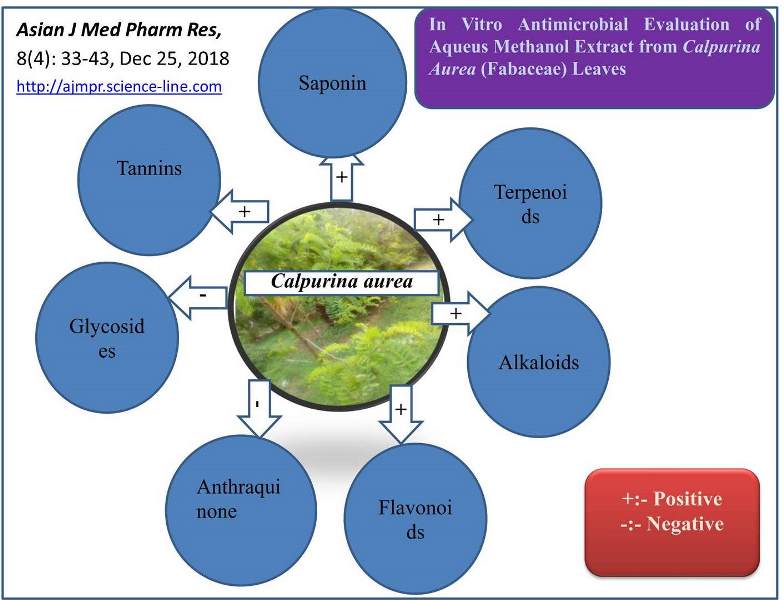
In Ethiopia, Calpurnia aurea is used for the treatment of syphilis, malaria, rabies, diabetes, hypertension, diarrhoea, leishmaniasis, trachoma, lymphatic filariasis, fungal diseases and different swellings. However, despite its traditional usage as an agent, there is limited information regarding the phytochemical and in vitro antimicrobial profile of the leaves of Calpurnia aurea. Calpurnia aurea leaves were collected from Gondar area, northern Ethiopia and dried under shed. The collected plant material were powdered using electrical grinder and then macerated with 99.5% methanol for 72 hours with mechanical shaking repeated three times and it was filtered through Whatman No.1 filter paper and the filtrate was dried using rotary evaporator at 500C. Preliminary phytochemical screening such as test for tannins, flavonoids, terpenoids, saponins, glycosides, alkaloids and anthraquinones were done using standard methods; antimicrobial activity by agar well diffusion and micro well dilution methods were performed. Calpurnia aurea leave contained tannins (+), terpenoids (+), saponins (+), flavonoids (+), alkaloids (+) but lacked glycosides and anthraquinone (-). The extracts of leaves of the plant indicated good antimicrobial activity in both crude and fractionate especially methanol extract against E. coli (ATCC 25922), S. auras (ATCC 29213) and S. typhi (ATCC 6539). It is evident from this study that the highest therapeutic efficacy possessing majority of secondary metabolites with strong antimicrobial property were present in leaves of Calpurnia aurea, which can be quantified for application in pharmaceutical industry for treatment of different disease.
Keywords: Antimicrobial Effect, Calpurnia Aurea, Phytochemicals
[Full text-PDF]
Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.